Is your VPS facing more downtime? Are you facing a high load even if no heavy processes are running? Are you worried about how to test if my VPS is oversold? Chances are your hosting provider is overselling the server.
This is the guide to test if VPS is oversold.
Overselling occurs when the hosting service sells more resources than the actual available resources. As a result, you can’t use the resources you pay for. It slows down your VPS or even causes downtime.
That’s why you need a proper step to test if the server is oversold.
Before that, let’s see why VPS providers oversell the servers.
Why do VPS providers oversell their servers?
A VPS is considered oversold when the hosting provider allocates more resources to the users than the actual available resources.
Let’s assume, a server has a total storage capacity of 16 TB and memory of 32 GB. So, the hosting provider can create 4 VPS of 4 TB storage each with 8 GB of RAM. However, they usually oversell it and offer more storage instead of 4.
This is where overselling is done.
Now, the question is why do VPS providers oversell their servers? That’s because hosting services work on stats and average usage of resources.
As a server admin, they can see server’s storage usage. If the average storage usage is 50%, it means that the average consumption of each VPS is just 2 TB out of 4. In this case, they have 16 TB of extra storage unused.
So, they oversell the server and offer 8 TB storage instead of 4.
By this calculation, the total allocated storage is 32 TB while the actual storage is just 16 TB. The problem arises when the total consumption of each VPS exceeds 16 TB. In that case, the server doesn’t physically have more storage to allocate.
The same happens with all the other resources. So, we can say that the hosting provider oversells their VPS because they don’t want to keep the unused resources as it is.
A few services like Kamatera provide “unlimited scaling” where their servers have hardware capability to add more storage. So, the team adds more drives if someone orders more storage.
How to test if my VPS is oversold?
Before running the test to see if your VPS is oversold, you need to ensure that your website is properly optimized. It’s not always your host’s fault if your website is running slow. At WebHostingAdvices, we have many tutorials on optimizing your website.
The simplest way to identify if the server is oversold is to monitor the downtime and slow speed. If your server never or rarely goes down, and your VPS always loads at maximum speed, you don’t need to worry about overselling.
It’s safe to say that your service isn’t oversold.
If you’re still unsure, you can use many of the following tests to check the overselling. Let’s start tests to see if the server is oversold.
Performance Monitoring
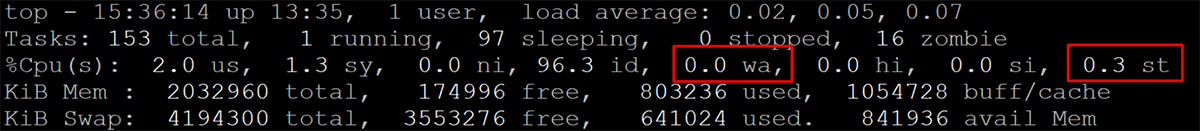
You can regularly monitor your VPS resources using commands like top, htop, etc.
Here’s a demonstration of the “top” command. You need to run it on the terminal of your VPS.
You will have to see two main factors here. “Wa” is waiting time which indicates that your VPS has to wait for the data to arrive. This means that the storage is limited. In the same way, you need to see “St”.
If “St” is higher, it means that a large amount of resources is being stolen from your allocated resources. So, the lower the “wa” and “st”, the better it is. These are the two primary factors you need to look for.
You need to ensure that these are consistently lower. There could be slight variations where the stealing might go higher. However, if the average is close to 0, your VPS isn’t oversold. Gridpane has explained all these commands thoroughly. You can check them out to know more.
Network Speed Tests
The next step is to regularly conduct network tests to see the allocated bandwidth (uplink). If you experience slower port speed, your VPS could be oversold.
1 Gbps is a good speed to start with. You also need to see if the port offered is the dedicated one or shared. If the port is shared with other people, the uplink you will get is slightly lower.
In the same way, you need to test the bandwidth port for each data center. You can use looking glass to test the network speed.
Benchmarking
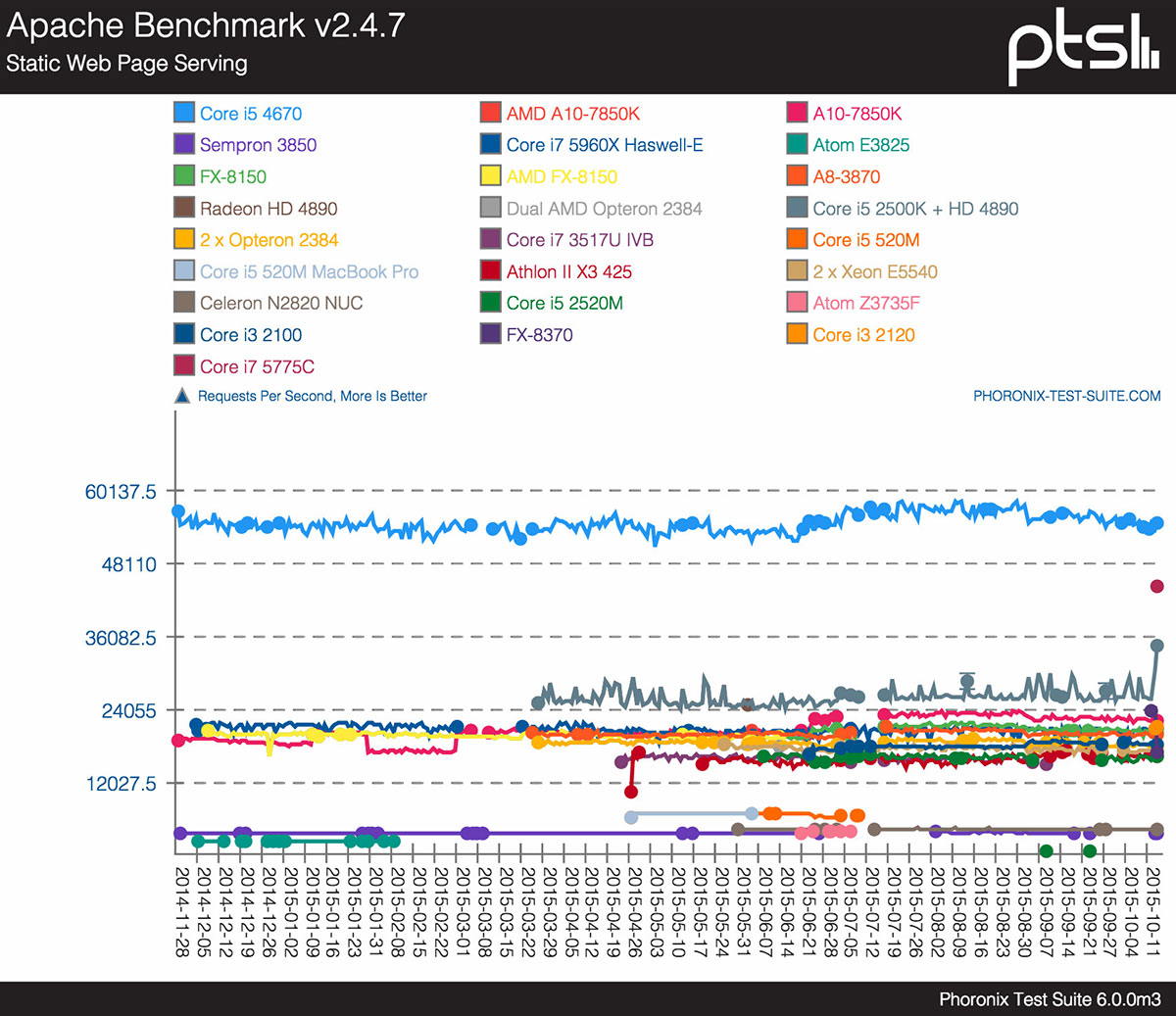
A harder approach to test if your VPS is oversold is to use benchmarking tools such as Phoronix Test Suite, Geekbench, Linuxbench, Unixbench, etc.
Ideally, you should check the benchmark against the specs your VPS provider promises. Check for consistent discrepancies. This may indicate overselling. A small disparity is not a big deal. However, if the same issue arises frequently, your VPS might be oversold.
Dream Offer
The line “VPS as low as shared hosting” looks attractive. However, it could not always perform. Quality comes in money. You either need to spend more on VPS instead of going with a $5 or $10 server, or you need to find the cheapest VPS.
For instance, Contabo offers high-spec CPU at a very low rate. However, there are good chances that the VPS is oversold. WebHostingAdvices always mentions the downside while we cover the cheap VPS list on our website.
Resource Guarantees
You need to look for “100% rescue guarantees” or a fixed-guarantee from the VPS before purchasing.
That’s why people prefer VPS with KVM or other virtualizations. Virtualization isolates the resources. Although it doesn’t completely remove the overselling issue.
Remember, it’s not just about saving your resources from others but also about the server not being oversold.
Customer Reviews
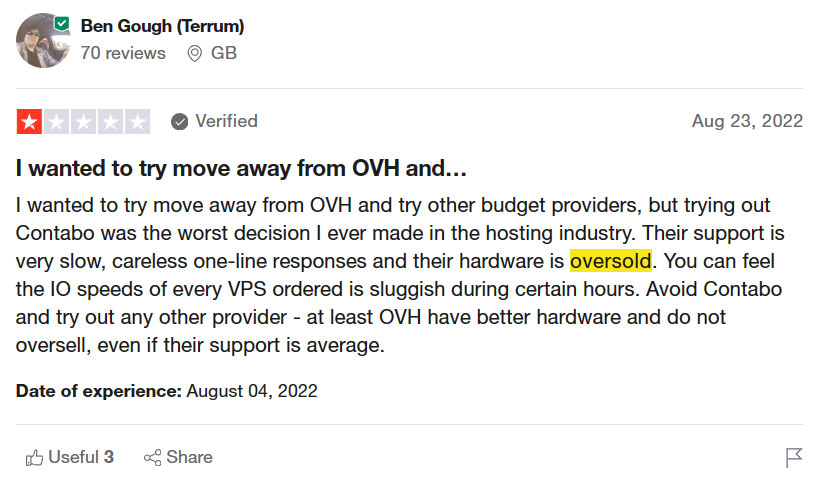
We are not talking about generic customer reviews on the hosting provider. Instead, you need to look for in-depth reviews about resources limitations, and performance, and try to identify other signs of overselling in those reviews.
Trustpilot allows you to search the reviews using keywords. You can use keywords such as resources, overselling, oversold, performance, etc. to identify if the server is oversold.
Make sure you try all the similar words such as oversold, overselling, over selling, etc.
Check Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Yet another way to get the best performance is to check Service Level Agreements (SLAs). The reputed VPS services offer 100% SLA. Even 99.9% will do for most people. This ensures that their services won’t be oversold.
How to test an oversold server?
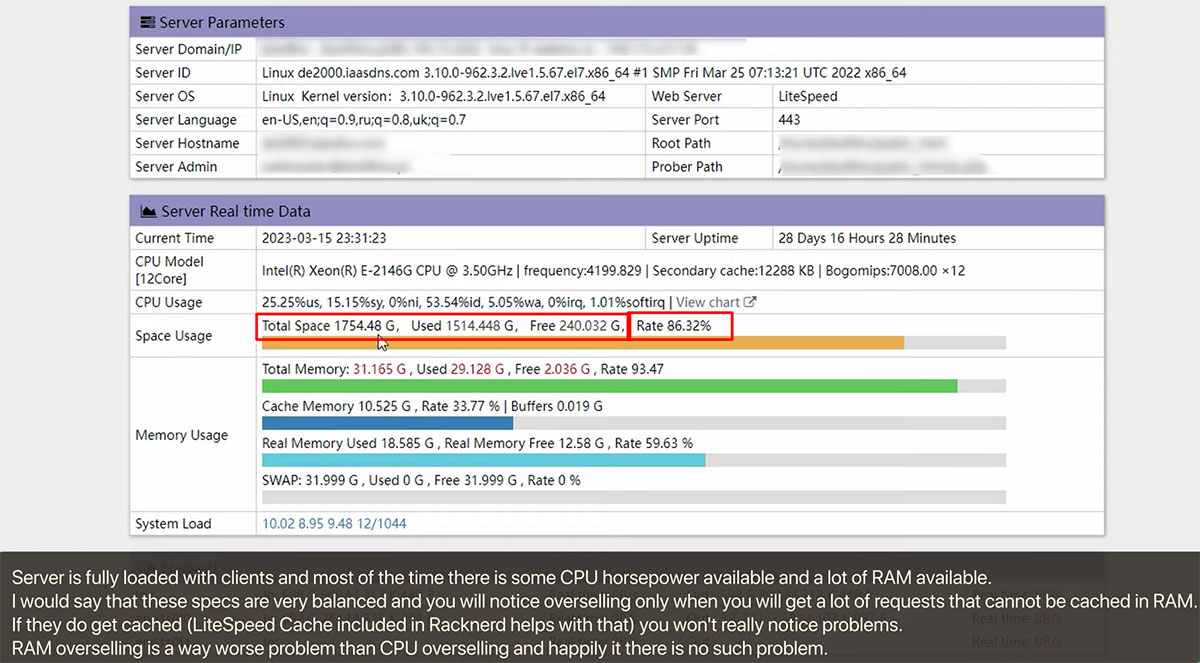
There are multiple ways to test an oversold server. You can use a script to get the real-time data of the server. LowEndBox shared a script that they used to measure the server load.
Let’s see the summary of the same.
The above screenshot tests the servers using a script. It’s just an example, you can use any script to test the load of the server including the performance monitoring tools we discussed earlier in our article.
The popular GitHub scripts for server testing include sysbench, stress-ng, etc.
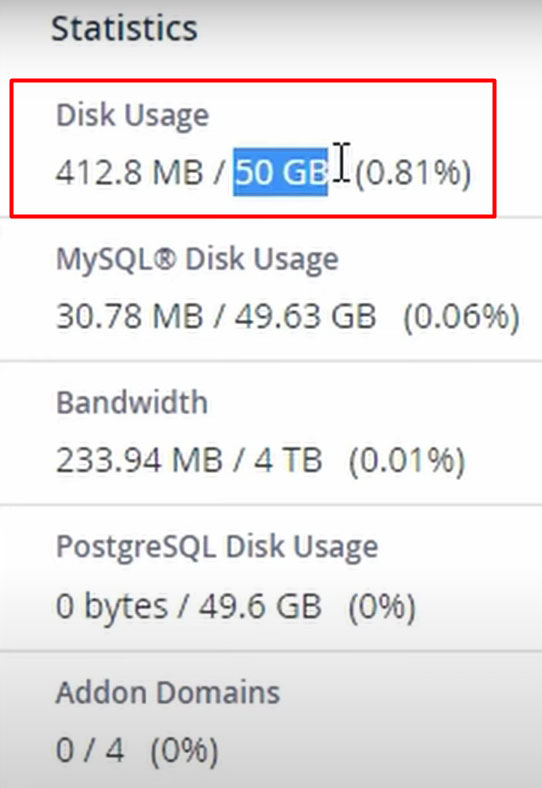
As you can see in the snapshot, the total storage available is only around 240 GB. There could be many more VPS servers hosted on the same server.
The person who used the above script was only using around 400 MB of storage out of the allocated 50 GB. Just assume that if they use 100% of their storage, the server would only have less than 190 GB of storage.
If 5 more people use 100% of their allocated storage, the storage of this server would be oversold. Now, if anyone tries to upload new files, they will get an error despite them having enough storage space.
For storage, it’s easier to identify if the server is oversold or not as you will start getting errors while uploading the files. However, you need to take extra steps when you want to test the CPU overselling.
That’s where you can’t 100% accurately say if the server is oversold.
To get maximum accuracy for CPU overselling, you can test your server with the maximum load possible. As mentioned in the above sections, there are specific tools that help you to test the CPU load.
When you test the server with maximum capacity, you will identify if there are any problems with the server.
What to do Next?
Contact the host and ask them to analyze the server. Here’s what you can ask them to do.
- Move to another physical server in the same company.
- Ask the hosting provider to increase IO.
- They can check the server to see if someone else is stealing the resources.
If it’s not possible, you can install “Redis” which is an in-memory database. It will help you in fixing your storage, bandwidth, RAM, etc. With this, the server uses a Redis cache instead of RAM.
Unfortunately, nothing can be done about the CPU.
The last option is to shift to a better VPS provider.
Conclusion
To summarize the solution for “how to test if my VPS is oversold”, you can tell if the server is oversold using various scripts and commands.
An easy way to identify the issue is to see if your server is down more often or if it takes too much time to load your websites despite doing all the optimizations.
It’s also worth noting that occasional downtimes are common due to software updates or traffic spikes. So, you need to check the average downtime.
Likewise, if your VPS resources are always in red, you can optimize your resources. We have an amazing guide on how to reduce IO usage on VPS. You can try optimizing it.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between an oversold and overloaded server?
An oversold server is when the hosting service sells more resources than the capacity of the server while an overloaded server is when all the VPS users use the maximum of their allocated resources.
How to ensure that your server is not oversold?
The only way to be 100% sure that your server is not oversold is to go with a dedicated server.
Alternatively, you can go with the VPS that guarantees to not oversell. The contract guarantee is one way of ensuring that the server is not oversold. Other than this, you will have to test the server manually.
Why is my VPS so slow?
There are many reasons for a slow VPS. One of them is when the VPS is oversold. Other than this, your websites might not have enough optimizations or the provider has not good enough quality.
Why do hosting providers oversell their servers?
Hosting providers know that most of their customers don’t utilize 100% of the allocated resources. So, the company promises and sells more resources than they can physically provide in order to make more money.